Point-in-time recovery EARLY ACCESS
Point-in-time recovery → across different products
To prevent data loss, YugabyteDB Aeon supports point-in-time recovery (PITR) and database cloning. When enabled for a database or keyspace, YugabyteDB takes a snapshot of the data once a day. Each snapshot maintains a continuous change history. You can then create a database clone at the current time or at a specific time in the past.
The clone is a zero-copy, independent writable clone of your database that you can use for the following:
-
Data recovery. To recover from data loss due to user error (for example, accidentally dropping a table) or application error (for example, updating rows with corrupted data), you can create a clone of your production database from a point in time when the database was in a good state. This allows you to perform forensic analysis, export the lost or corrupted data from the clone, and import it back to the original database.
-
Development and testing. Because the two databases are completely isolated, you can experiment with the cloned database, perform DDL operations, read and write data, and delete the clone without impacting the original or affecting its performance.
You can change the retention window for the clone. The default is two days.
For more information on database cloning, refer to Instant database cloning.
For more information on PITR in YugabyteDB, refer to Point-in-time recovery.
To configure point in time recovery, and create a clone at a point in time, go to the cluster Backups tab and choose Point in time Recovery.
Clone a database
You can clone a database at the current time, without configuring PITR.
To clone a database or keyspace at the current point in time, do the following:
-
Navigate to Databases.
-
Select the database or keyspace.
-
Click Database Actions and choose Clone to Point-in-time.
-
Provide a name for the clone.
Note that to clone a database or keyspace at an earlier point in time, you must first enable PITR.
-
Click Clone.
When finished, the cloned database is listed in the Databases list.
Enable PITR
To clone a database or keyspace at an earlier point in time, you must first enable PITR for the database or keyspace.
You enable PITR for databases and keyspaces as follows:
-
Navigate to the cluster Backups tab and choose Point in time Recovery to view a list of the databases and keyspaces already enabled for PITR, if any.
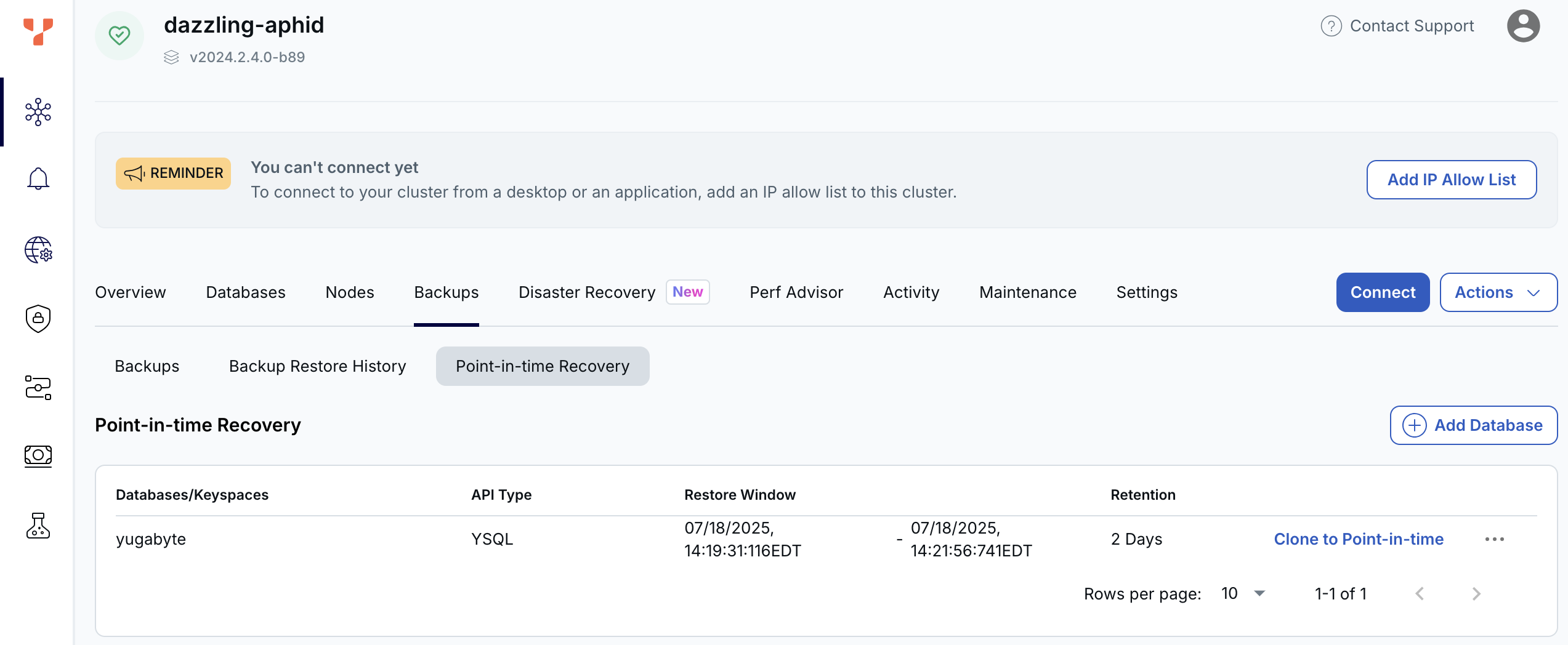
If there are currently no databases or keyspaces enabled for PITR, a message is displayed.
-
Click Add Database or, if there are currently no databases or keyspaces enabled for PITR, Enable Point-in-time Recovery.
-
Select the databases or keyspaces for which to enable PITR.
-
Click Next.
-
Set the retention window for PITR.
-
Click Enable Point-in-time Recovery.
The database or keyspace is added to the Point-In-Time Recovery list.
Clone to a point in time
If PITR has been enabled, you can clone a database or keyspace at a specific point in time as follows:
-
Navigate to Point-in-time Recovery.
-
Find the database or keyspace you want to recover and click Clone to Point-in-time.
-
Provide a name for the clone.
-
Specify the time at which to create the clone.
-
Click Clone.
When finished, the cloned database is listed in the Databases list.
Change the retention
You can change the PITR retention window for a database or keyspace as follows:
-
Navigate to Point-in-time Recovery.
-
Find the database or keyspace, click the three dots (...) to display its actions, and choose Edit Retention.
-
Specify the retention window.
-
Click Save.
Disable PITR
You can disable PITR for a database or keyspace as follows:
-
Navigate to Point-in-time Recovery.
-
Find the database or keyspace, click the three dots (...) to display its actions, and choose Disable Point-in-Time Recovery.
Caveats and limitations
Enabling PITR impacts both disk consumption and performance. Keep in mind the following:
-
When you increase the number of stored snapshots (by increasing the retention period of the snapshots), you also increase the amount of space required for the database. The amount of storage required also depends on the workload. When enabled, monitor your storage consumption alerts and add disk space or reduce the retention period if necessary.
-
If you notice an impact on performance, refer to Operational considerations for guidance about further tuning.
In addition to the snapshot retention period, YugabyteDB allows you to adjust the snapshot interval, which in YugabyteDB Aeon is fixed at 24 hours.
Database clones do not initially use added disk space, but they do create an independent set of logical tablets. If you are at or have exceeded the tablet peer limit, you cannot create clones. If you hit or exceed the limit due to tablets that a clone is creating, then operations on the clone will fail.